Horses are magnificent creatures, and their anatomy is equally fascinating. In this article, we’ll delve into the incredible world of horse anatomy, unveiling 11 captivating facts that might surprise you.
Table of Contents:
1. Equine Muscles: Powerhouses of Strength
Horses are renowned for their strength and endurance. Their muscular system is a marvel of nature, with some muscles accounting for up to 60% of their body weight. These muscles enable them to perform a wide range of activities, from racing to carrying heavy loads.
One remarkable fact is that horses have more than 700 individual muscles, all working in harmony to provide the power needed for their movements. The strong and well-developed muscles in their hindquarters, known as the “engine” of the horse, are particularly vital for propulsion.
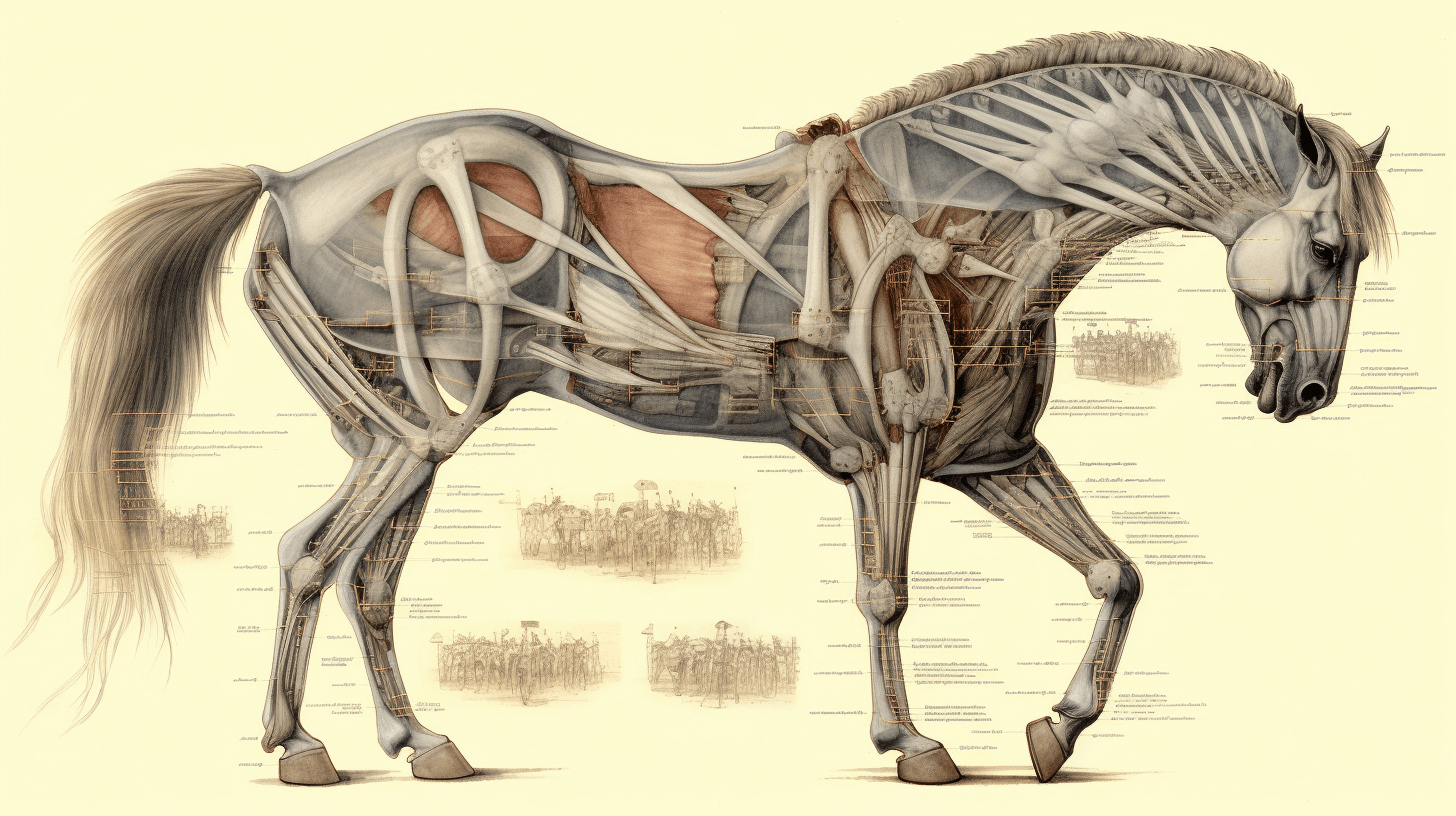
2. The Elegant Skeletal Structure
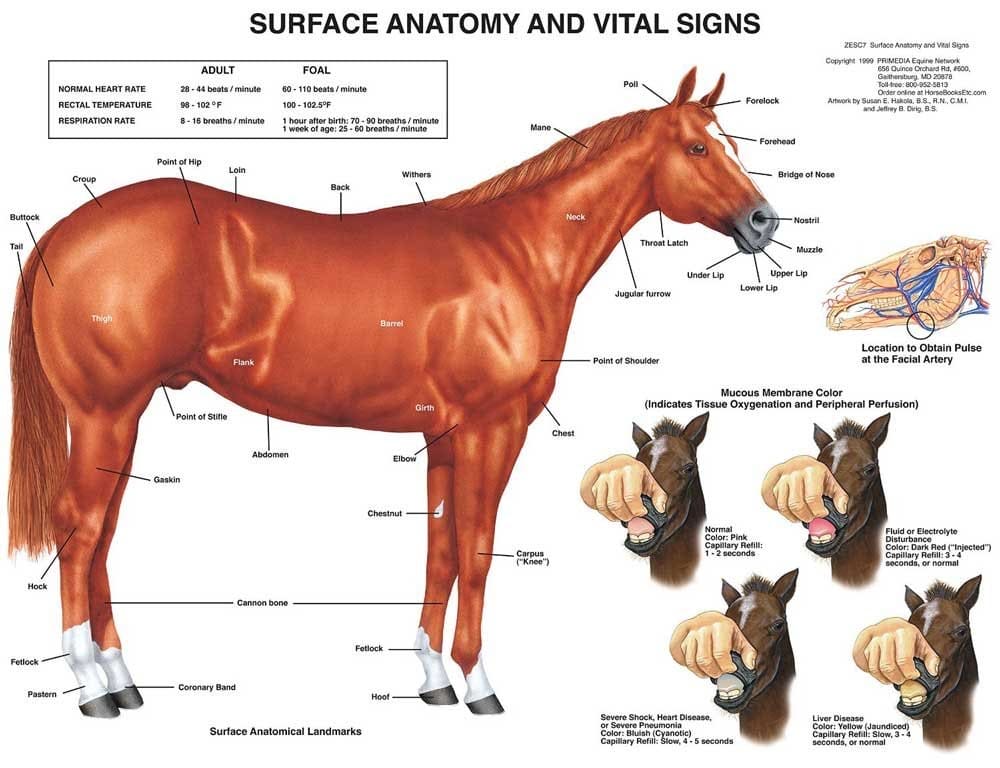
The skeleton of a horse is a masterpiece of design, tailored for speed and agility. They have approximately 205 bones in their body, and each bone has a specific function. The long, slender bones in their legs, for example, contribute to their grace and swiftness.
One of the most interesting features of a horse’s skeleton is its ability to absorb shock. This is crucial for minimizing the impact on their joints and bones while galloping or jumping. The flexibility of their spine also aids in their fluid movements.
3. Hooves: The Foundation of Every Step
A horse’s hooves are a critical part of their anatomy, providing support and protection. Each hoof is made up of a tough outer shell called the hoof wall, which covers a softer inner structure. This design helps distribute the horse’s weight evenly and absorb shock.
Interestingly, a horse’s hoof continues to grow throughout its life. Regular maintenance, including trimming and shoeing, is essential to keep them healthy and balanced.
4. The Amazing Respiratory System
A horse’s respiratory system is finely tuned to support their demanding physical activities. Their large nostrils allow for ample airflow, while their deep lungs have a vast surface area for efficient oxygen exchange.
During strenuous exercise, a horse can take in up to 180 liters of air per minute. This exceptional oxygen intake fuels their muscles and enables them to maintain high levels of performance.
5. The Complex Digestive Process
Horses are herbivores with a unique digestive system adapted to their diet. They have a large cecum, a pouch-like structure, where microbial fermentation takes place. This process allows them to break down fibrous plant material and extract nutrients.
However, it also means that horses are susceptible to digestive issues, such as colic, if their diet or feeding routine is not carefully managed.
6. The Sensitive Nervous System
Horses have a highly developed nervous system that plays a crucial role in their behavior and responses to the environment. Their keen sense of hearing and ability to detect vibrations in the ground make them incredibly aware of their surroundings.
Additionally, horses are known for their flight response, a survival instinct that makes them react quickly to perceived threats. Understanding their nervous system is essential for effective horse training and handling.
7. Vision: A Horse’s Superpower
A horse’s vision is nothing short of extraordinary. Their large eyes are positioned on the sides of their head, providing them with a panoramic field of view that spans nearly 350 degrees. This wide vision angle helps them spot predators even while grazing.
Horses also have excellent night vision, thanks to a high number of rod cells in their retinas. This adaptation makes them well-suited for both daytime and nighttime activities.
8. Ears: Tuned into the World
Horses have highly sensitive ears that can rotate nearly 180 degrees. This allows them to pinpoint the source of sounds and communicate with other horses through subtle ear movements.
Their acute hearing is another survival advantage, as it helps them detect predators and sense danger before it’s too late.
9. The Heart: Keeping the Beat
A horse’s heart is a remarkable organ that ensures proper blood circulation during physical exertion. During intense exercise, a horse’s heart rate can reach up to 240 beats per minute, efficiently pumping oxygenated blood to their muscles.
The cardiovascular system of a horse is finely tuned to meet the demands of their active lifestyle, and it’s one of the reasons they can perform such strenuous activities.
10. Unique Teeth and Digestion
Horses have a set of specialized teeth designed for their herbivorous diet. Their teeth continually erupt throughout their life, compensating for the wear caused by grinding fibrous plant material.
Understanding a horse’s dental health is essential to ensure they can chew their food properly and maintain good overall health.
11. Skin and Coat: More Than Meets the Eye
A horse’s skin and coat are not just about aesthetics; they play crucial roles in their well-being. The skin acts as a protective barrier, keeping out harmful microorganisms and regulating body temperature.
Their coat, which can vary greatly in color and texture, provides insulation and protection from the elements. The shedding of their winter coat in spring is a fascinating natural process influenced by changes in daylight.
Conclusion
Horse anatomy is a testament to the marvels of nature. These creatures are not only beautiful but also incredibly well-adapted to their environment. From their muscles and bones to their digestion and sensory organs, every aspect of their anatomy contributes to their success as magnificent animals.
Now that you’ve explored these 11 fascinating facts about horse anatomy, you can appreciate these incredible creatures on a whole new level.
FAQs About Horse Anatomy
1. What is the total count of bones present in a horse’s skeletal structure?
A horse’s skeleton typically consists of 205 bones.
2. What makes a horse’s vision so special?
Horses have a wide field of vision, approximately 350 degrees, which allows them to detect predators and potential threats easily.
3. Do all horse breeds have the same number of teeth?
No, the number of teeth can vary slightly among different horse breeds, but on average, they have 36-44 teeth.
4. How fast can a horse’s heart beat during exercise?
During intense exercise, a horse’s heart can beat at a rate of 240 beats per minute or even higher.
5. What is the cecum, and why is it important for digestion?
The cecum is a part of the horse’s digestive system responsible for breaking down fibrous plant material. Its significance in aiding the digestive process is paramount.